About Me
I am a Ph.D. candidate in Bioengineering at University of Maryland College Park, adviesd by Prof. Yang Tao in the Bio-imaging and Machine Vision Lab. I received my M.S. degrees from the Graduate Institue of Biomedical Electronics and Bioinformatics at National Taiwan University, where I was advised by Prof. Kung-Bin Sung in Biomedical Optical Spectroscopy and Imaging lab. I earned my B.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from National Taiwan University.
Research
My research focuses on applying machine learning and computer vision to biomedical imaging and signal processing. My goal is to enhance the efficiency and accessibility of applications such as medical diagnosis, therapeutic monitoring, and bioengineering systems. To achieve this vision, I have worked across a diverse range of domains, as outlined below:
• Human Pose Estimation & Motion Analysis: EgoFall [ICASSP'24], AutoComPose [ICCV'25]
• Optical & Hyperspectral Biosensing: Hyperspectral Imaging[EMBC'21], Microscopy[BOE'20], Diffuse Reflectance/Near-infrared Spectroscopy[Photonics'19] [BOE'18] [Frontiers in Optics / Laser Science'18] [SPIE'18]
• Bioengineering & Other Applications: ShellCollect [IEEE Access'24], Mechanobiology[Scientific Report'20]
Publications
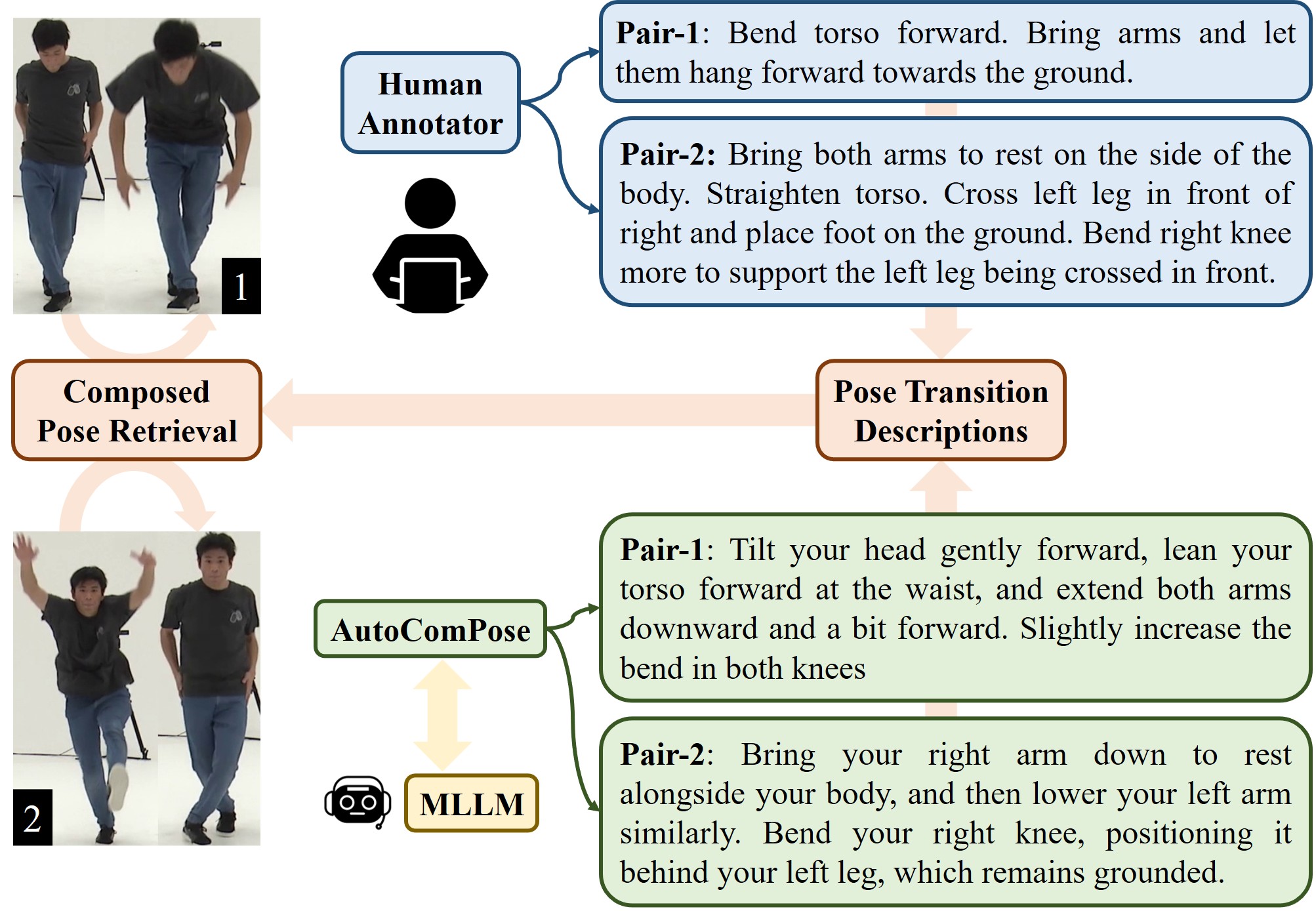
AutoComPose: Automatic Generation of Pose Transition Descriptions for Composed Pose Retrieval Using Multimodal LLMs
Yi-Ting Shen*, Sungmin Eum*, Doheon Lee, Rohit Shete, Chiao-Yi Wang, Heesung Kwon, and Shuvra S. Bhattacharyya (* equal contribution)
ICCV 2025
[arXiv]
We introduce AutoComPose, the first framework to automatically generate pose transition annotations using multimodal large language models, significantly improving composed pose retrieval performance while reducing reliance on costly human labeling.

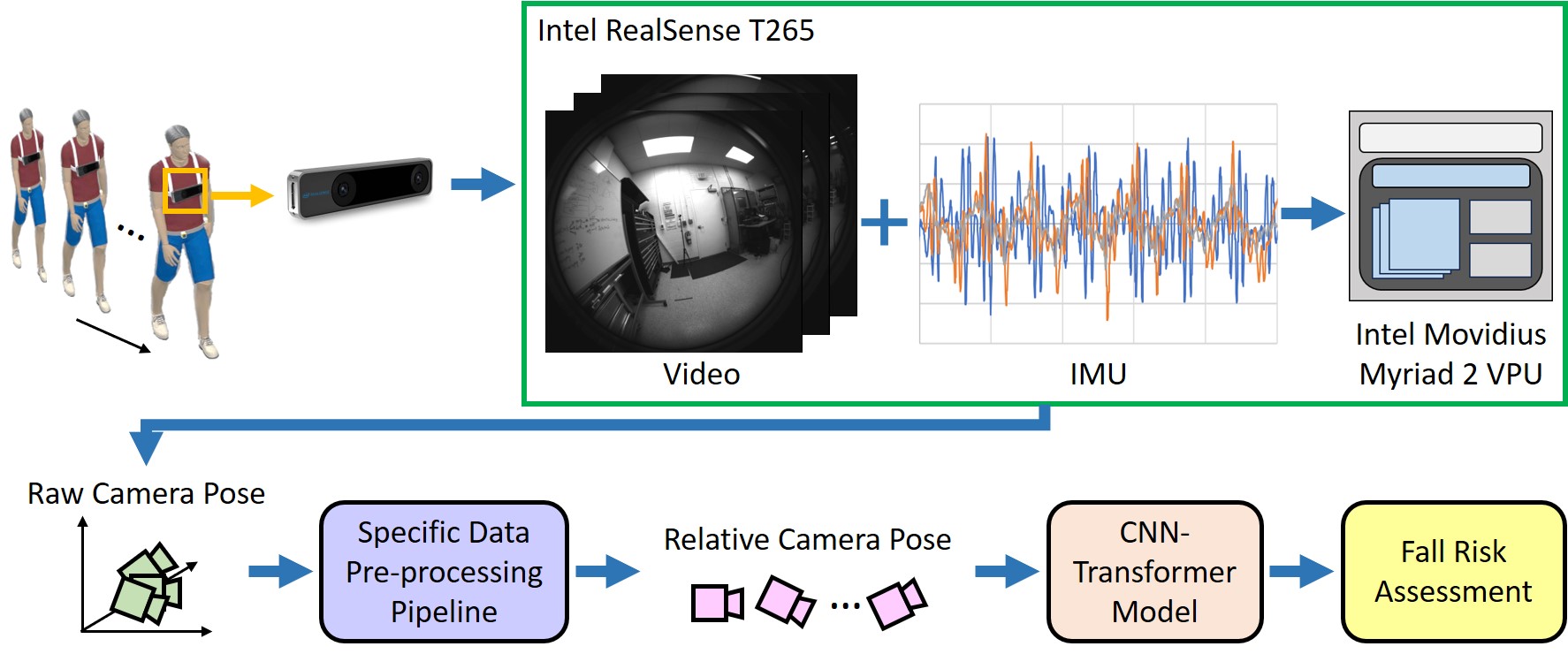
EgoFall: Real-time Privacy-Preserving Fall Risk Assessment with a Single On-Body Tracking Camera
Chiao-Yi Wang, Faranguisse Kakhi Sadrieh, Yi-Ting Shen, Giovanni Oppizzi, Li-Qun Zhang, Yang Tao
IEEE TNSRE 2025
[Paper]
This paper presents EgoFall, a real-time, privacy-preserving fall risk assessment system using a chest-mounted tracking camera and a lightweight CNN-Transformer model to identify direction-specific instability walking patterns.

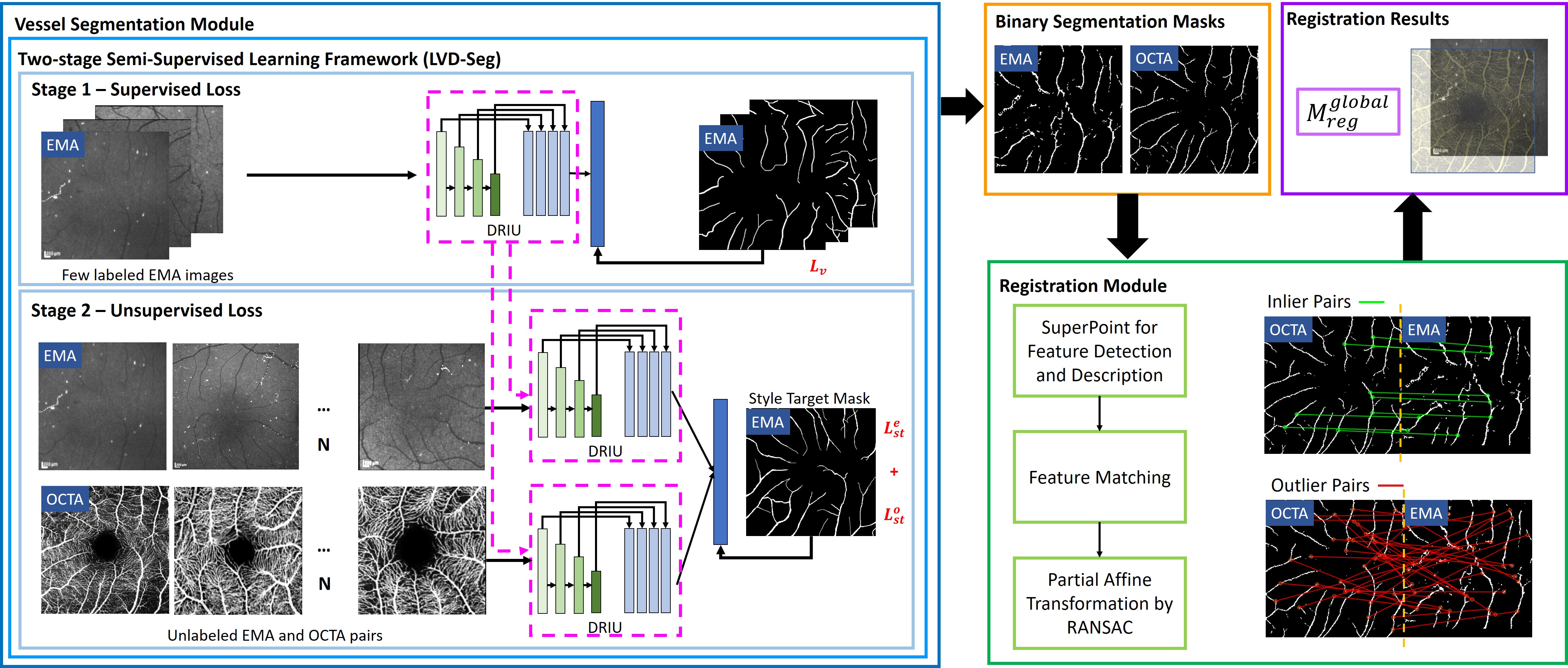
MEMO: dataset and methods for robust multimodal retinal image registration with large or small vessel density differences
Chiao-Yi Wang, Faranguisse Kakhi Sadrieh, Yi-Ting Shen, Shih-En Chen, Sarah Kim, Victoria Chen, Achyut Raghavendra, Dongyi Wang, Osamah Saeedi, and Yang Tao
Biomedical Optics Express 2024
[Paper][Dataset]
We propose VDD-Reg, a segmentation-based deep-learning framework for multimodal retinal image registration that can robustly register two imaging modalities despite vessel density differences.

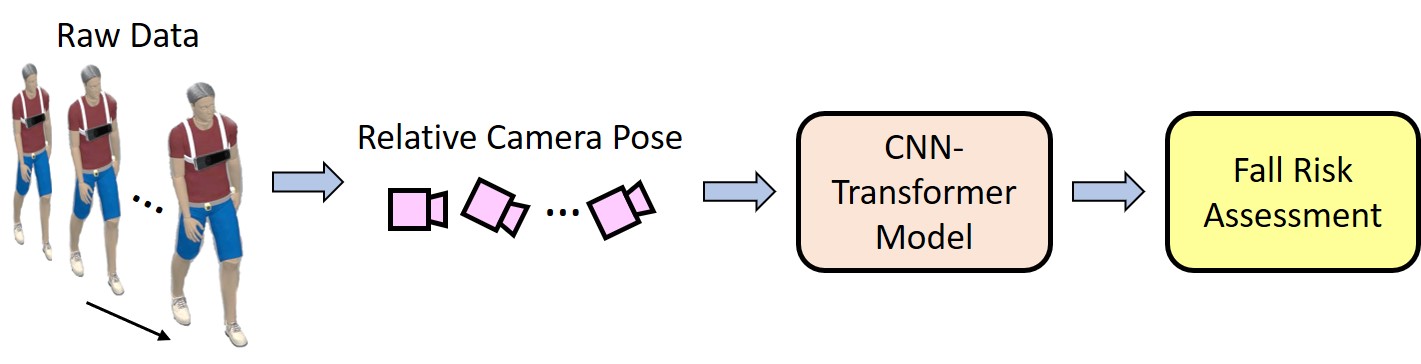
Real-Time Privacy-Preserving Fall Risk Assessment with a Single Body-Worn Tracking Camera
Chiao-Yi Wang, Faranguisse Kakhi Sadrieh, Yi-Ting Shen, Giovanni Oppizzi, Li-Qun Zhang, Yang Tao
ICASSP 2024
[Paper]
We propose EgoFall, a real-time, privacy-preserving fall risk assessment system using a chest-mounted tracking camera and a lightweight CNN-Transformer model, enabling personalized fall prevention without the need for multiple wearable sensors.

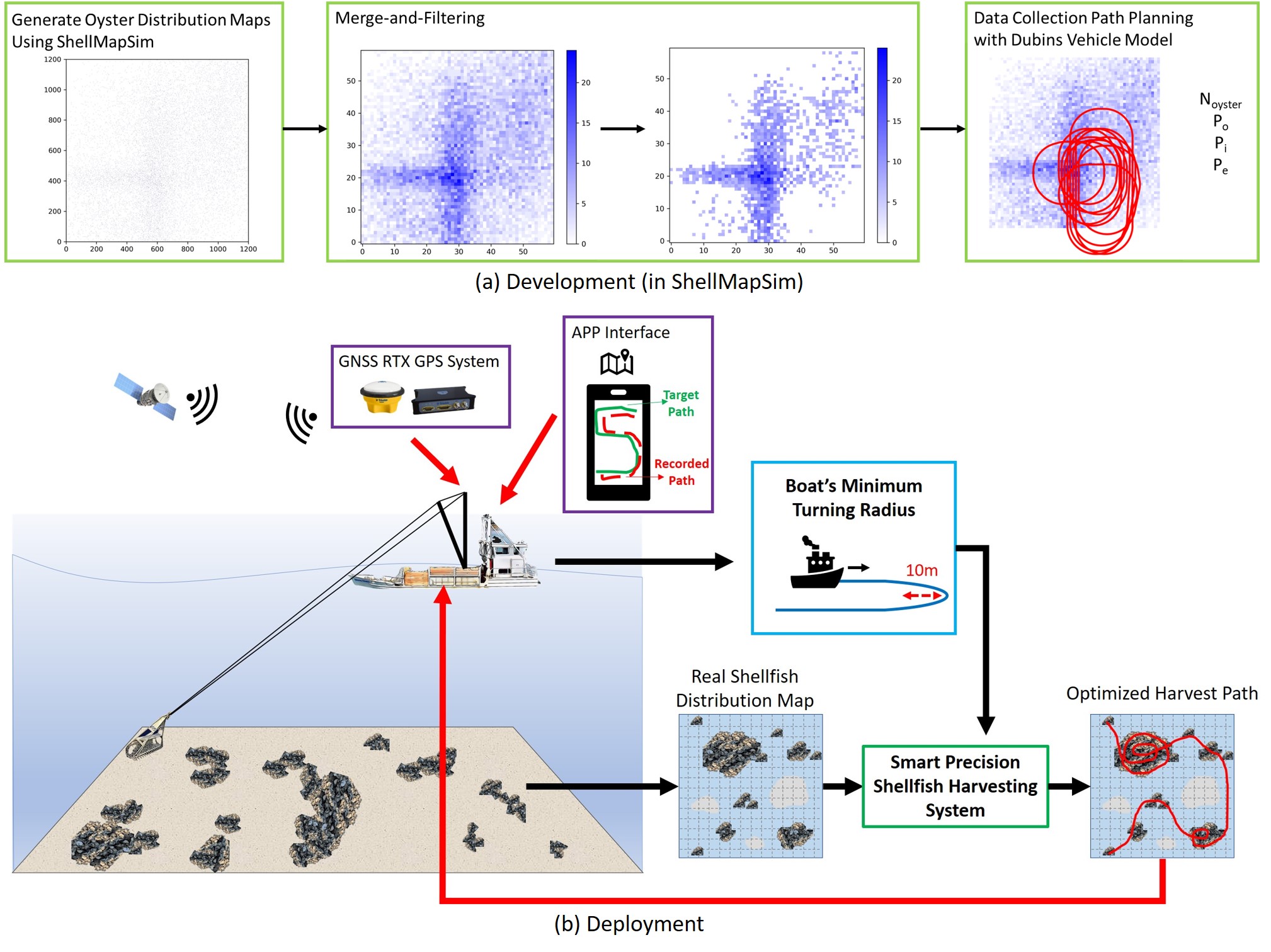
ShellCollect: A Framework for Smart Precision Shellfish Harvesting Using Data Collection Path Planning
Chiao-Yi Wang, ADP Guru Nandhan, Yi-Ting Shen, Wei-Yu Chen, Sandip Sharan Senthil Kumar, Alexander Long, Alan Williams, Gudjon Magnusson, Allen Pattillo, Don Webster, Matthew Gray, Miao Yu, Yang Tao
IEEE Access 2024
[Paper]
We introduce ShellCollect, the first smart precision shellfish harvesting framework that plans efficient dredging paths based on underwater oyster distributions using a novel VNS-based algorithm.

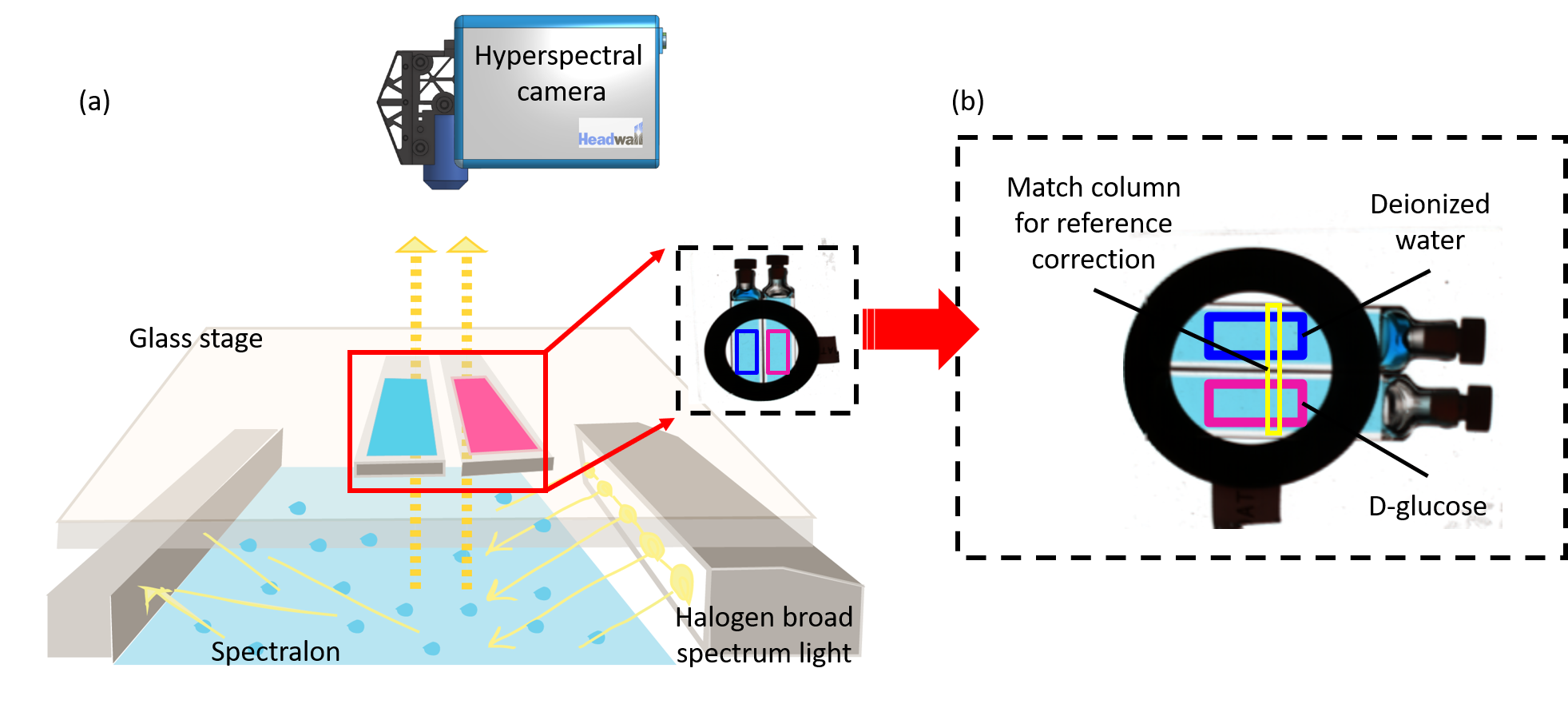
Prediction of Aqueous Glucose Concentration Using Hyperspectral Imaging
Chiao-Yi Wang, Anjana Hevaganinge, Dongyi Wang, Mohamed Ali, Maurizio Cattaneo, Yang Tao
IEEE EMBC 2021
[Paper]
We demonstrate a non-invasive method for predicting aqueous glucose concentration using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging (HSI) combined with Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR), achieving accurate results across a wide concentration range.

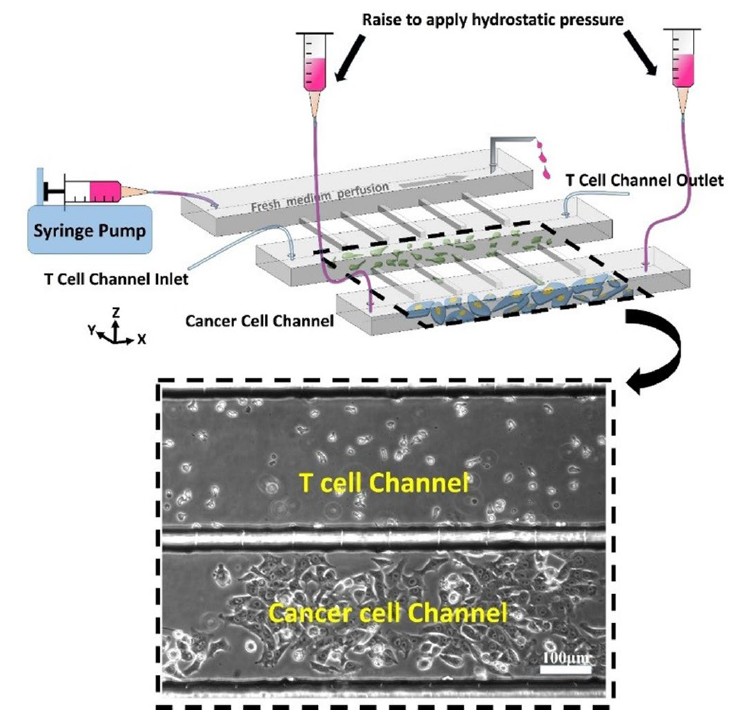
Evaluation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated anticancer response against tumor interstitium-simulating physical barriers
Shu-Ching Chen, Po-Cheng Wu, Chiao-Yi Wang, Po-Ling Kuo
Scientific Reports 2020
[Paper]
Using a microfluidic platform that mimics tumor physical barriers, we show that while antigen-specific CTLs retain cytotoxic efficacy, increased interstitial fluid pressure hinders their infiltration, underscoring the need to consider tumor microenvironments in immunotherapy design.

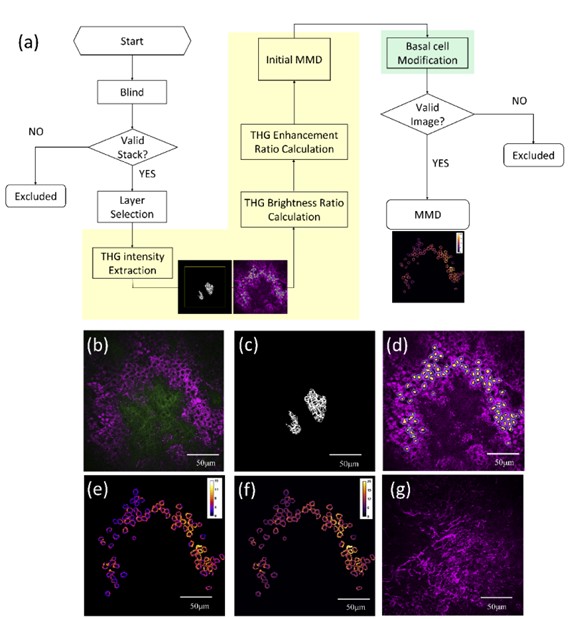
Slide-free clinical imaging of melanin with absolute quantities using label-free third-harmonic-generation enhancement-ratio microscopy
Chi-Kuang Sun, Pei-Jhe Wu, Sheng-Tse Chen, Yu-Hsiang Su, Ming-Liang Wei, Chiao-Yi Wang, Hao-Cheng Gao, Kung-Bing Sung, Yi-Hua Liao
Biomedical Optics Express 2020
[Paper]
We present a label-free third-harmonic-generation (THG) enhancement-ratio microscopy technique that enables in vivo 3D imaging of melanin distribution in human skin with microscopic detail and absolute mass density, offering a powerful tool for noninvasive diagnosis and long-term treatment assessment of melanin-related disorders.

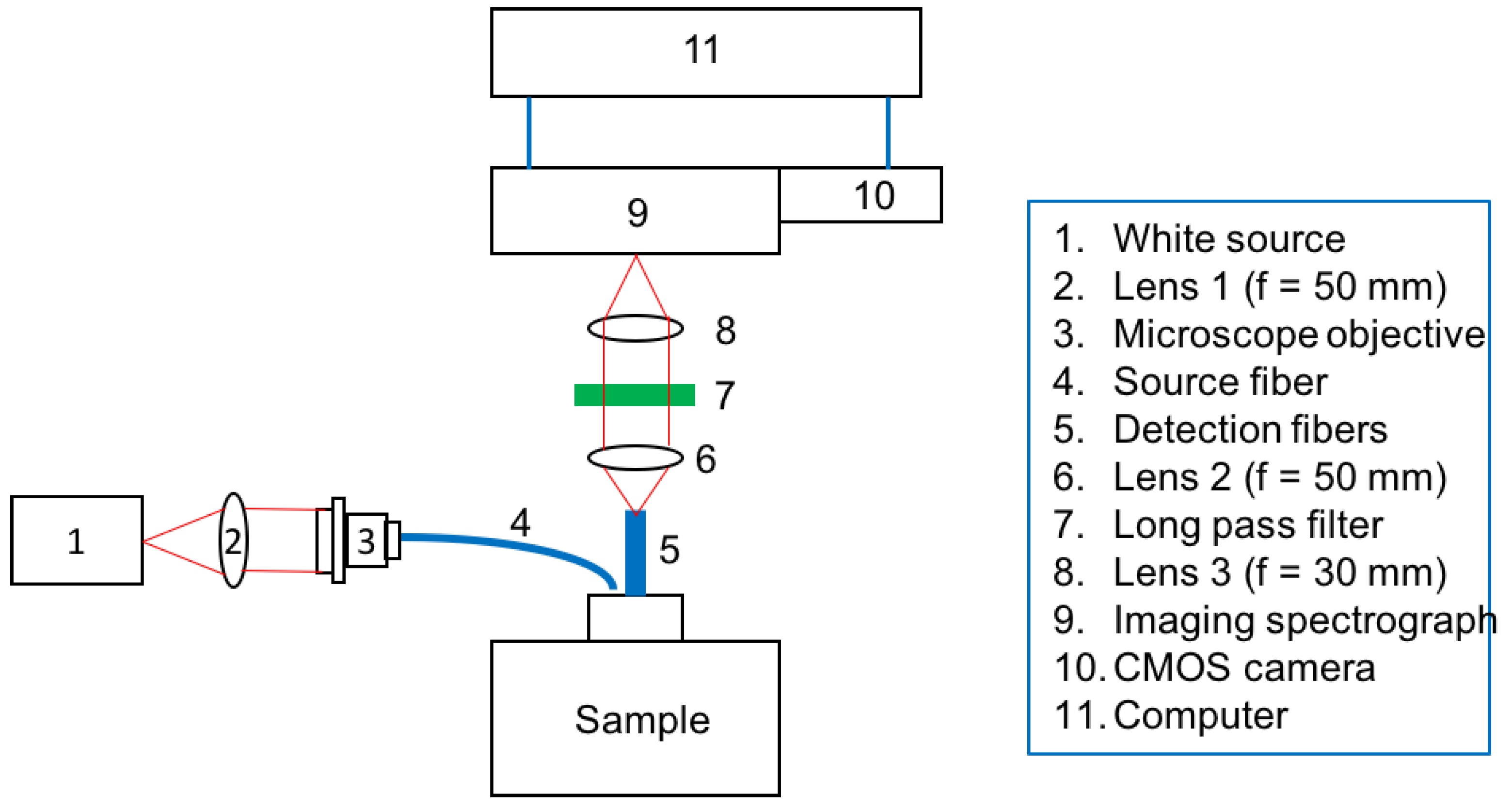
Validation of an Inverse Fitting Method of Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy to Quantify Multi-Layered Skin Optical Properties
Chiao-Yi Wang, Tzu-Chia Kao, Yin-Fu Chen, Wen-Wei Su, Hsin-Jou Shen, Kung-Bin Sung
Photonics MDPI 2019
[Paper]
We propose a fast and accurate inverse fitting method using neural networks to quantify key skin optical properties and chromophore concentrations without requiring prior knowledge of epidermis thickness, enabling practical and cost-effective in vivo skin analysis.

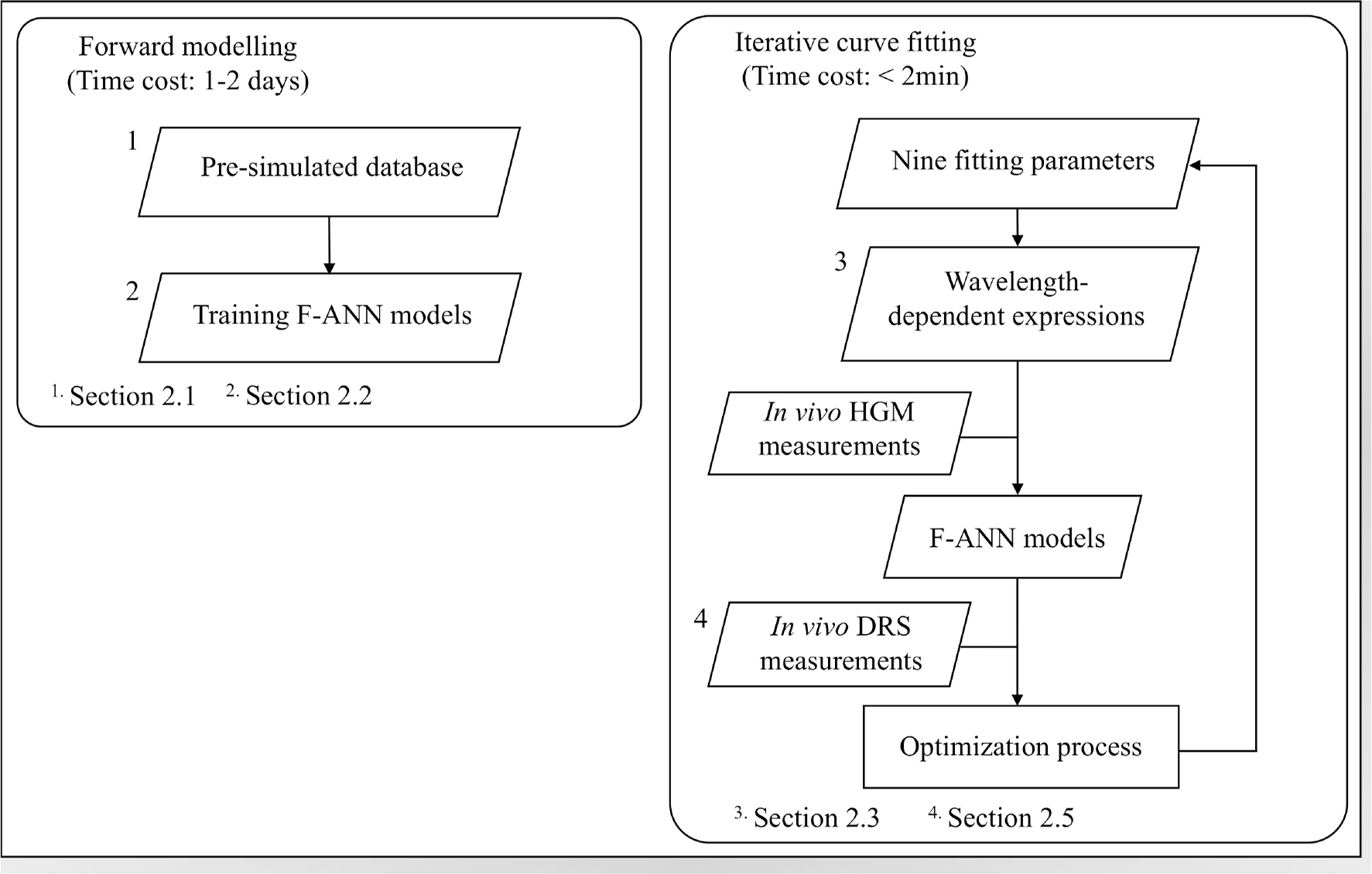
Modelling spatially-resolved diffuse reflectance spectra of a multi-layered skin model by artificial neural networks trained with Monte Carlo simulations
Sheng-Yang Tsui, Chiao-Yi Wang, Tsan-Hsueh Huang, Kung-Bin Sung
Biomedical Optics Express 2018
[Paper]
We propose a neural network-based modeling method to efficiently and accurately extract chromophore concentrations and oxygen saturation from spatially-resolved diffuse reflectance spectra of multilayered skin, outperforming GPU-accelerated Monte Carlo simulations in both speed and fitting accuracy.

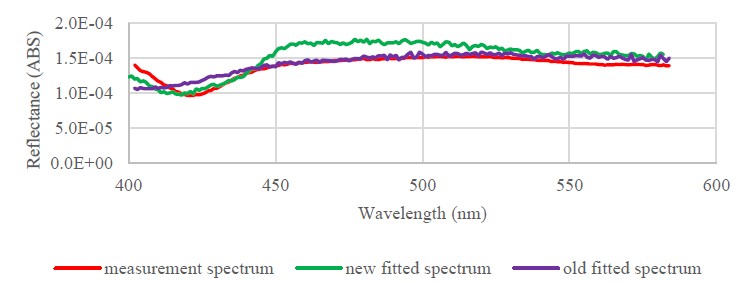
Improved Inverse Two- Layered Monte Carlo Fitting of In-vivo Skin Diffuse Reflectance Spectra
Chiao-Yi Wang, Ting-Xuan Lin, Kung-Bin Sung
Frontiers in Optics / Laser Science 2018
[Paper]
We present an improved inverse Monte Carlo fitting method for reliably extracting optical coefficients of the epidermis and shallow dermis from in-vivo skin reflectance spectra, achieving fitting errors below 13%.

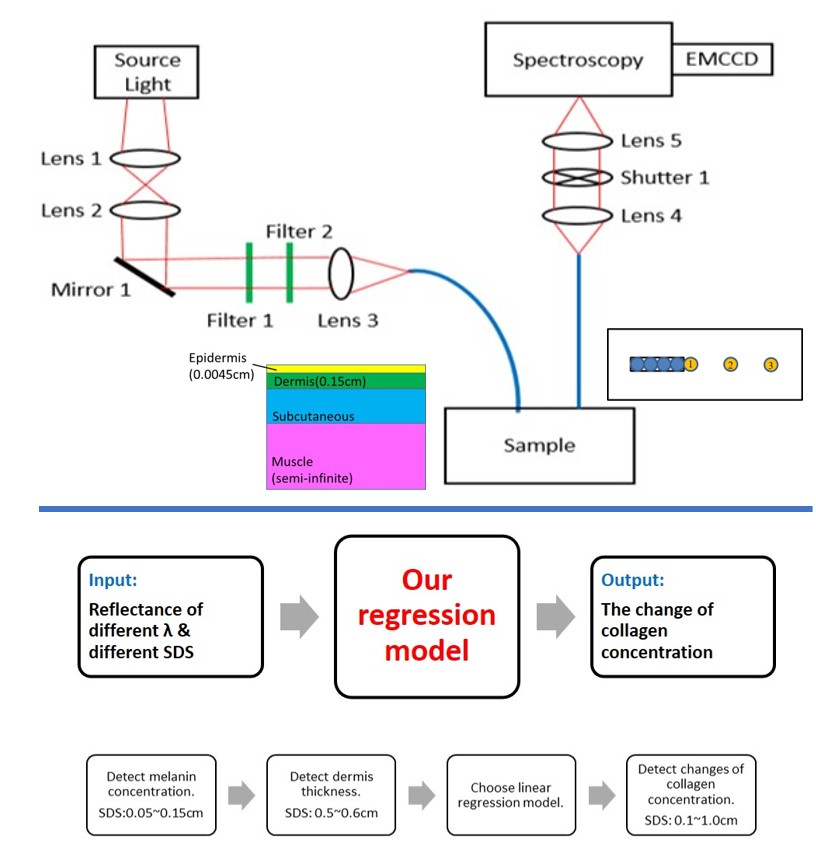
Developing visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy to detect changes of the dermal collagen concentration
Chiao-Yi Wang, Andy Ying Chi Liao, Kung Bin Sung
SPIE 2018
[Paper]
We developed a cost-effective, hand-held system using Monte Carlo simulations and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy to detect in vivo changes in dermal collagen concentration, accounting for the influence of underlying fat and muscle layers to improve measurement accuracy.

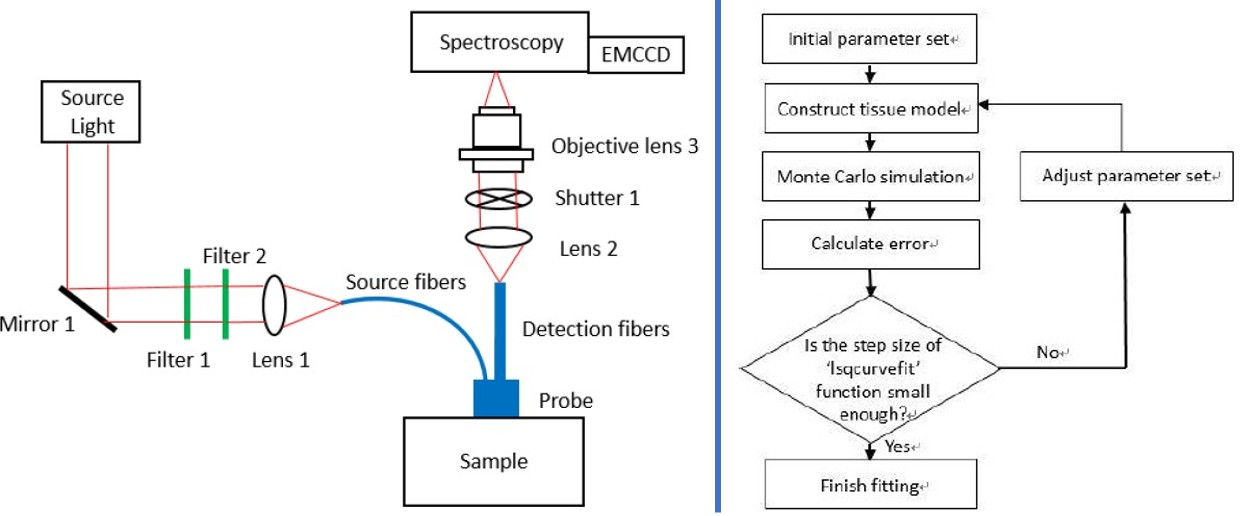
In vivo measurements of optical properties of human muscles with visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy
Chiao-Yi Wang, Ting Wen Yu, Kung Bin Sung
SPIE 2018
[Paper]
We used in-vivo diffuse reflectance spectroscopy with an inverse Monte Carlo model to estimate wavelength-dependent absorption and scattering coefficients of human muscles, offering more accurate optical property measurements than traditional ex-vivo methods.